Volatility Explained in Simple Words
Each of us knows that the prices in shops are not static: they can rise or fall, although they do rise in most cases.

Sometimes you come to a shop and see that the price of your favorite can of beer has risen. You come there the next day and see the price being even higher.
In such cases, it makes you involuntarily wonder: What the hell! Why does the price rise so quickly?
To put it simply, volatility means the rate at which the price of our beer can rises.
It can be measured both as a percentage and in monetary units.
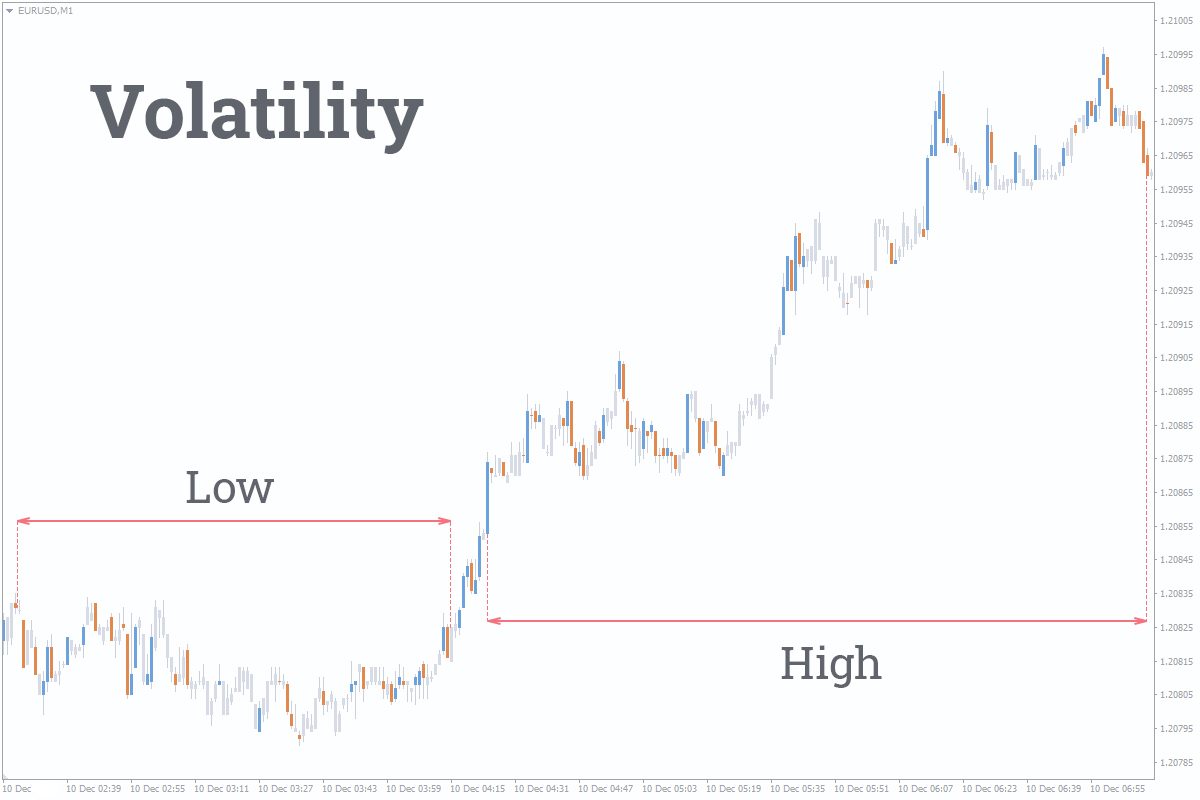
If one present volatility as a currency chart, it will look like this:
Volatility is often associated with the price fluctuations or the amplitude of the price movements. It can be very clearly seen in the picture above.
Volatility plays a very crucial role in risk assessment for financiers. For example, if it’s too high, they try to reduce the volume of their transactions.
It may seem that volatility is a bad thing, but it's not. After all, the higher it’s, the larger the potential earnings, as well as losses, in the Forex market.
On the other hand, if there has been a decline in volatility, asset (commodity) is not of interest anymore, and investors switch to more volatile financial instruments.
You might be interested in the Most and Least Volatile Currency Pairs on Forex.
Why does volatility change? Volatility, like price, almost never stands still. This is explained by a simple formula: demand=supply; if there is a trading imbalance, the price begins to move, while volatility increases.